When it comes to choosing monitors, most users only care about the brand and size, and often ignore the importance of parameters such as the panel, resolution, refresh rate, and color gamut. However, the indicators and parameters of monitors are so complex that it takes some time to learn and master them.
「Size」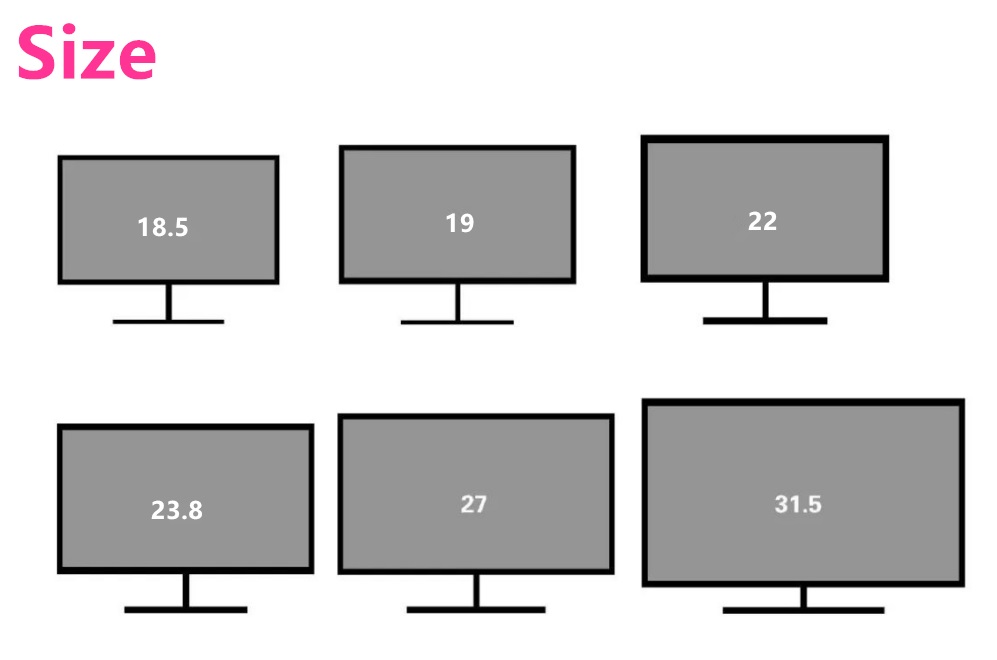
7/8/9/10/12/15/17/19/22/27 different size of monitors, is that the bigger size the better?
Generally speaking, 7-22 inch monitors are suitable for commercial and industrial usage; 24-27 inch displays are suitable for daily office and entertainment; 27-32 inches are suitable for games and editing. The size of the monitor should also consider personal needs and resolution requirements.
「Resolution」

1080P/FHD. 2K/QHD, 4-8K/UHD
Resolution mainly refers to the pixels on the screen. Under the premise of the same unit area, the higher the resolution, the more delicate the display effect. Common ones are 1920×1080 (1K), 2560×1440 (2K), and 3840×2160 (4K). However, it does not mean that the higher the resolution, the better. You also need to consider whether your graphics card can handle it. Generally speaking, 2K is chosen for office games, and 4K is chosen for design and editing.
「Refresh rate」
60hz, 144hz, 165hz, 240hz
The refresh rate refers to the number of times the screen refreshes per second. The higher the refresh rate, the better the image stability and transition effect. Generally speaking, 60Hz is the basic standard, suitable for daily use; 144Hz and above are e-sports level, suitable for playing high frame rate games.
「Response time」

1m, 3ms, 5ms, 8ms, 10ms
The response time of the monitor generally refers to the grayscale response time (Grey to Grey, or GTG). The shorter the response time, the lower the picture delay, and the ghosting phenomenon will be greatly reduced when playing games. The response time of 5ms is completely enough to take into account watching videos, playing small games, and editing. The response speed of 4ms and 3ms is enough to deal with most FPS games.
「Color gamut」
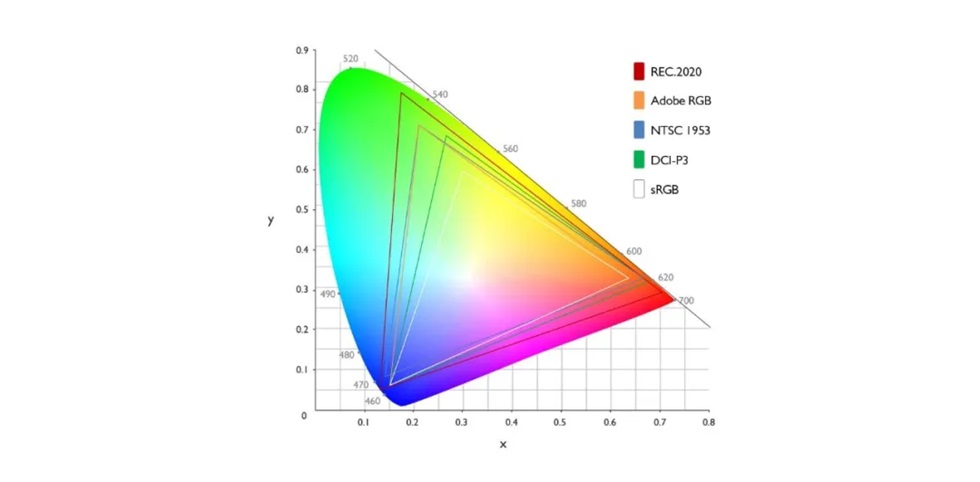
100%SRGB. 75%NTSC
Color gamut refers to the range of color. Common color gamut standards include sRGB, DCI-P3, Adobe RGB, etc. In industries such as image design, printing, and film and television, color gamut properties are important considerations because they require high color reproduction. For professional design, 100% sRGB color gamut coverage is generally required.
「Color accuracy」
AE/JNCD (display and real gap)
Color accuracy is an indicator of color accuracy, indicating the deviation between the displayed color and the standard color. The smaller the value, the better. Color accuracy ΔE<2 is the standard for professional displays. The color accuracy of the display can be calibrated by a colorimeter, such as the Red Spider screen colorimeter.
「Color depth」

8bit. 10bit
If the color gamut represents the breadth of color, then the color depth represents the color depth, which usually has a depth of 8bit or 10bit. The greater the color depth, the more colors are displayed, which is reflected in the more natural and smoother gradient color transition. In the field of graphic design, it is necessary to fine-tune and calibrate the colors, and at this time, a high-color-depth monitor is needed; in general office and gaming scenarios, an 8-bit color-depth monitor is sufficient to meet the needs.
「Screen brightness」
Unit: nits
The higher the brightness of the monitor, the brighter the colors and the better the display effect. Low: 250cd/㎡, enough: 300cd/㎡, very good: 350cd/㎡+
「Contrast」

Static contrast
Contrast is the difference between the brightest white and the darkest black on the display. The higher the contrast, the richer the color levels that can be displayed. Common contrast ratios are 1000:1, 1500:1, and 3000:1. It should be noted that the contrast of the monitor generally refers to the static contrast, and the dynamic contrast does not have much reference value for comparison.
「Panel」

OLED > mini LED > IPS > VA > TN
The common LCD panels at present are VA and IPS, and TN has been eliminated. VA has low cost and is more suitable for curved screens; IPS has a wide viewing angle and strong color accuracy, and is the first choice for mainstream monitors. OLED has absolute advantages in contrast and color vividness; while mini LED will perform better in brightness and is cheaper than OLED. IPS is still the mainstream in the market.
「Synchronization technology」
FreeSync vs G-SYNC
The common G-Sync and FreeSync technologies play an important role in improving the game experience of players. They are both display technologies used to reduce screen tearing, reduce input delay and optimize game fluency.
「Interface」
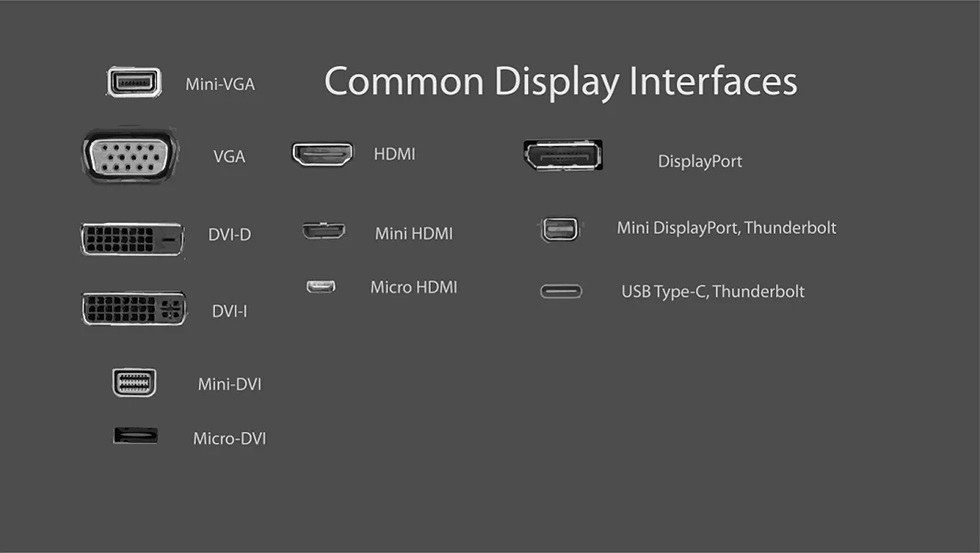
VGA, DVI, HDMI, DP, Type-c
VGA and DVI are old interfaces, HDMI and DP are mainstream interfaces, and Type-c is a slightly more expensive interface. If you want a good display effect, it is recommended to choose HDMI2.0 and above or DP1.4 and above.